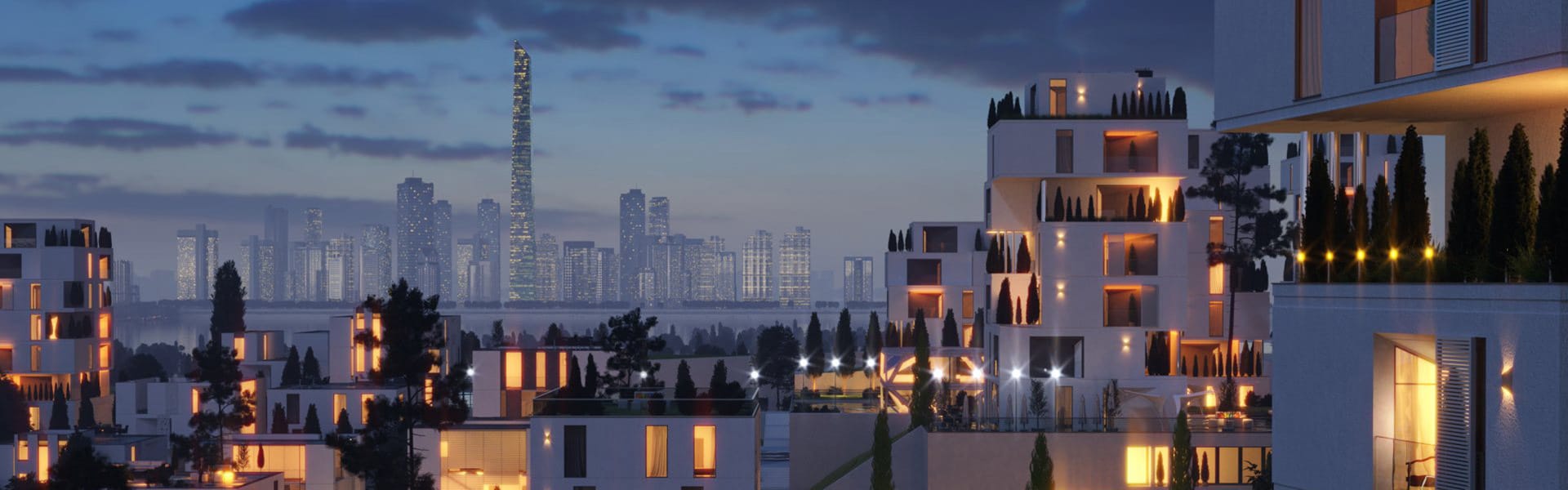
Dive into the similarities and differences between architectural models and renders, and learn how they can be used to bring your designs to life.
Architectural models and architectural renderings are important tools in visualizing and communicating design concepts. While architectural models are physical representations of buildings or structures, architectural renderings are digital visualizations created using software. In this article, we will explore the characteristics, types, creation process, pros and cons, as well as the complementary roles of both in visualization.
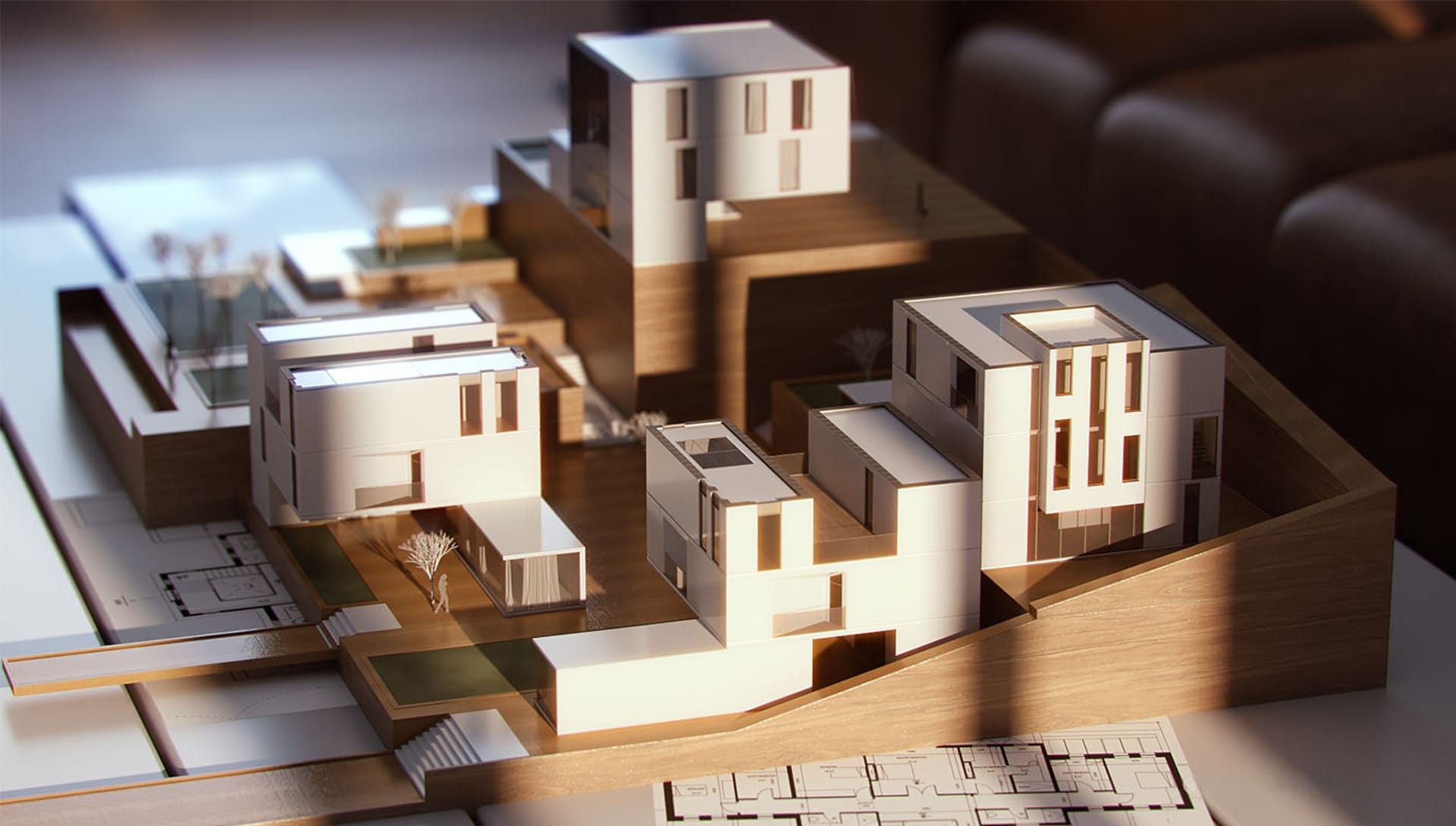

What is an architectural model?
An architectural model is a physical representation of buildings or structures that allows designers, clients, stakeholders, and team members to visualize and understand design concepts. The model can be created using various materials such as wood, cardboard, plastics, foam boards, and more. It plays a significant role in the design process by providing a tangible representation of spatial elements, form, scale, and design details.
Main characteristics
An architectural model possesses several key characteristics that contribute to its significance in the whole architecture and design process:
- Physicality: Architectural models exist in the physical world, allowing viewers to interact with them and gain a better understanding of the design.
- Scale: Models are created to a specific scale, enabling designers to showcase the proportions and dimensions of the actual building or structure.
- Representation of spatial elements: Models depict spatial relationships, interior layouts, exterior forms, and other design elements, helping stakeholders visualize the final outcome.
- Communication tool: Models serve as effective communication tools, allowing designers to convey design ideas, concepts, and details to clients, stakeholders, and team members.
- Educational and planning purposes: Architectural models are used in education, urban planning, and historical preservation to study and analyze designs, evaluate spatial relationships, and explore design alternatives.
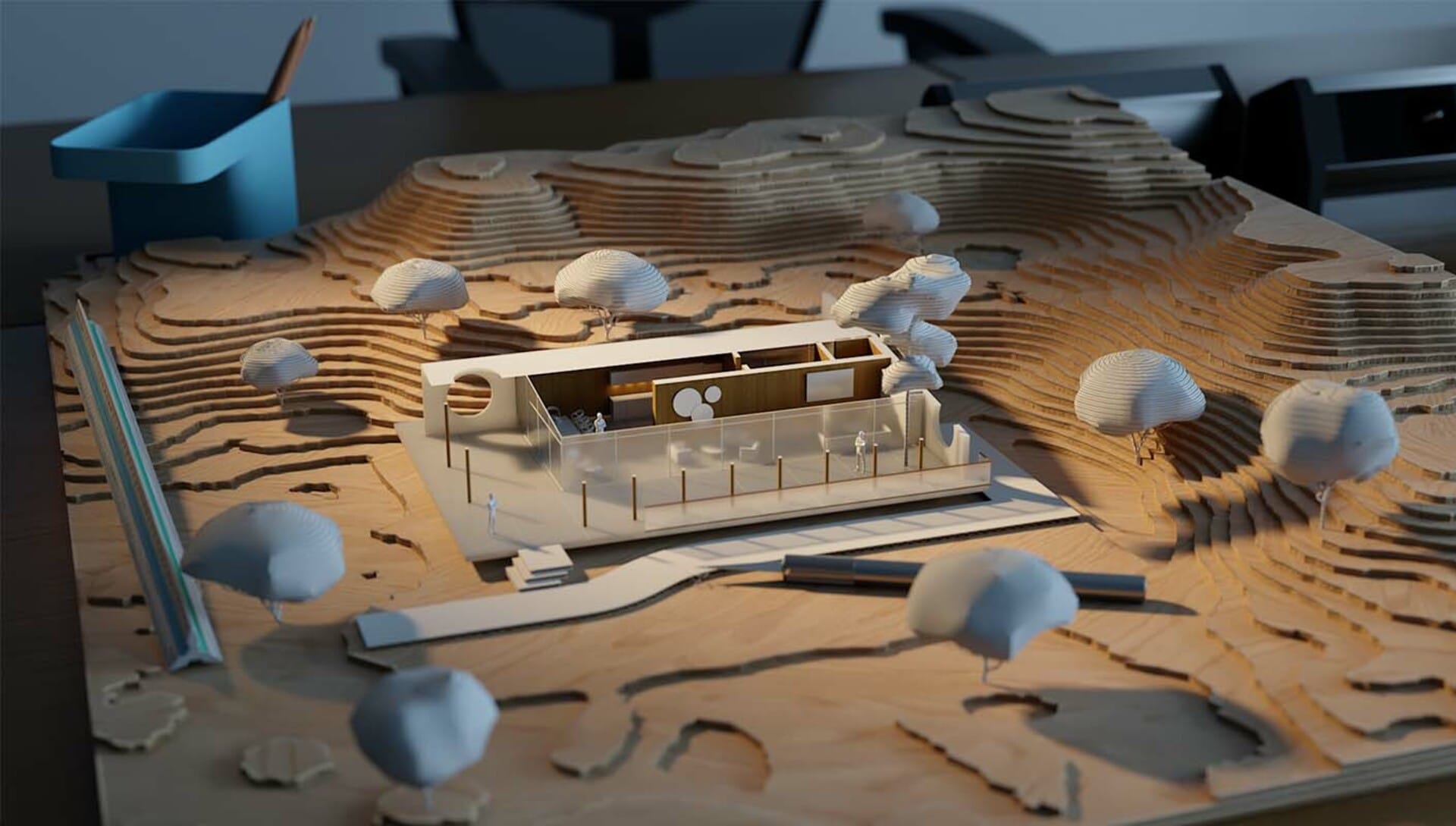

Types of architectural models
There are different types and scales of architectural models, each serving a specific purpose:
Physical architectural models
This type of architectural model is a physical representation or working design model constructed using materials like wood, cardboard, plastics, and more. Such models provide a tangible and interactive experience, allowing viewers to examine the design from different angles and perspectives.
Physical models are often used in presentations, exhibitions, and client meetings to showcase design concepts and spatial relationships. Their scale plays a crucial role, as it accurately represents the proportions and dimensions of the model making the actual building or structure.
Conceptual models
A conceptual model is created in the early stages of the design phase to explore ideas and concepts. It's often abstract and focused on visualizing design principles and initial architectural concepts.
Conceptual models help designers and clients understand the overall direction of the initial project stage and explore different possibilities during the design phase before moving forward with detailed development.
Functional models
Functional building models are often used to represent the operational design aspects. They demonstrate how a building or structure functions in real-world scenarios, showcasing elements such as circulation, lighting, ventilation, and more. Functional models are particularly useful in architectural design related to infrastructure, transportation, and urban planning.
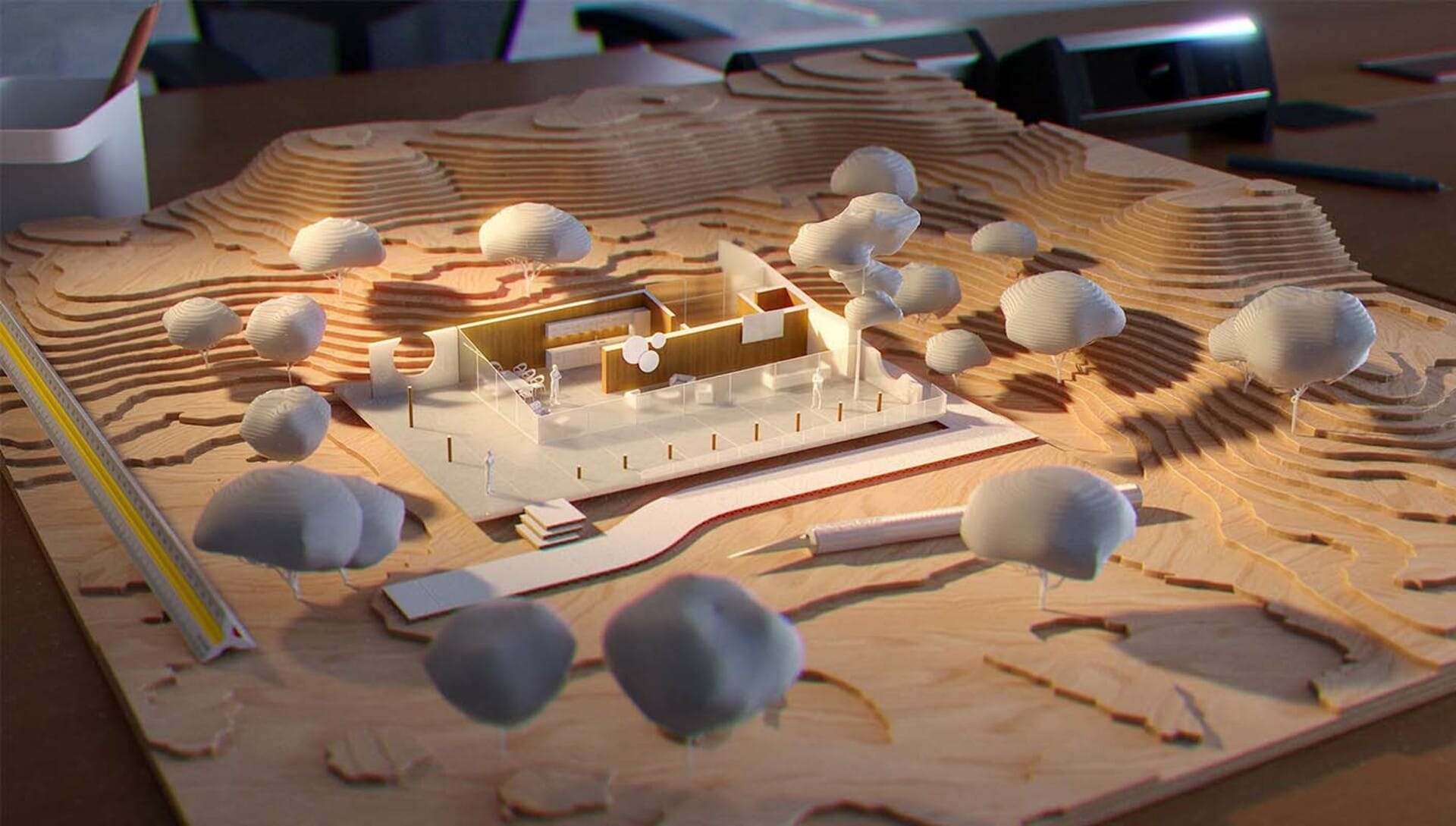

How to create an architectural model
Creating an architectural scale model often involves several steps and collaboration between architects, model makers, and designers. The model making process typically includes:
- Design development: Architects develop the design concept and spatial layout of the building or structure.
- Scale determination: The appropriate scale for the architectural model is determined based on the design's size and complexity.
- Material selection: Model makers choose the materials for constructing the model, considering factors such as durability, ease of manipulation, and aesthetic qualities.
- Model construction: The model is constructed using the chosen materials, following the design specifications and scale. Techniques such as cutting, gluing, painting, and detailing are employed to bring the model to life.
- Finishing touches: The model is refined and detailed, adding elements such as landscaping, furniture, and other design features to enhance its realism and visual appeal.
- Presentation: The completed model is presented to clients, stakeholders, or used for educational purposes, allowing viewers to engage with the design and gain a better understanding of its spatial qualities and aesthetics.
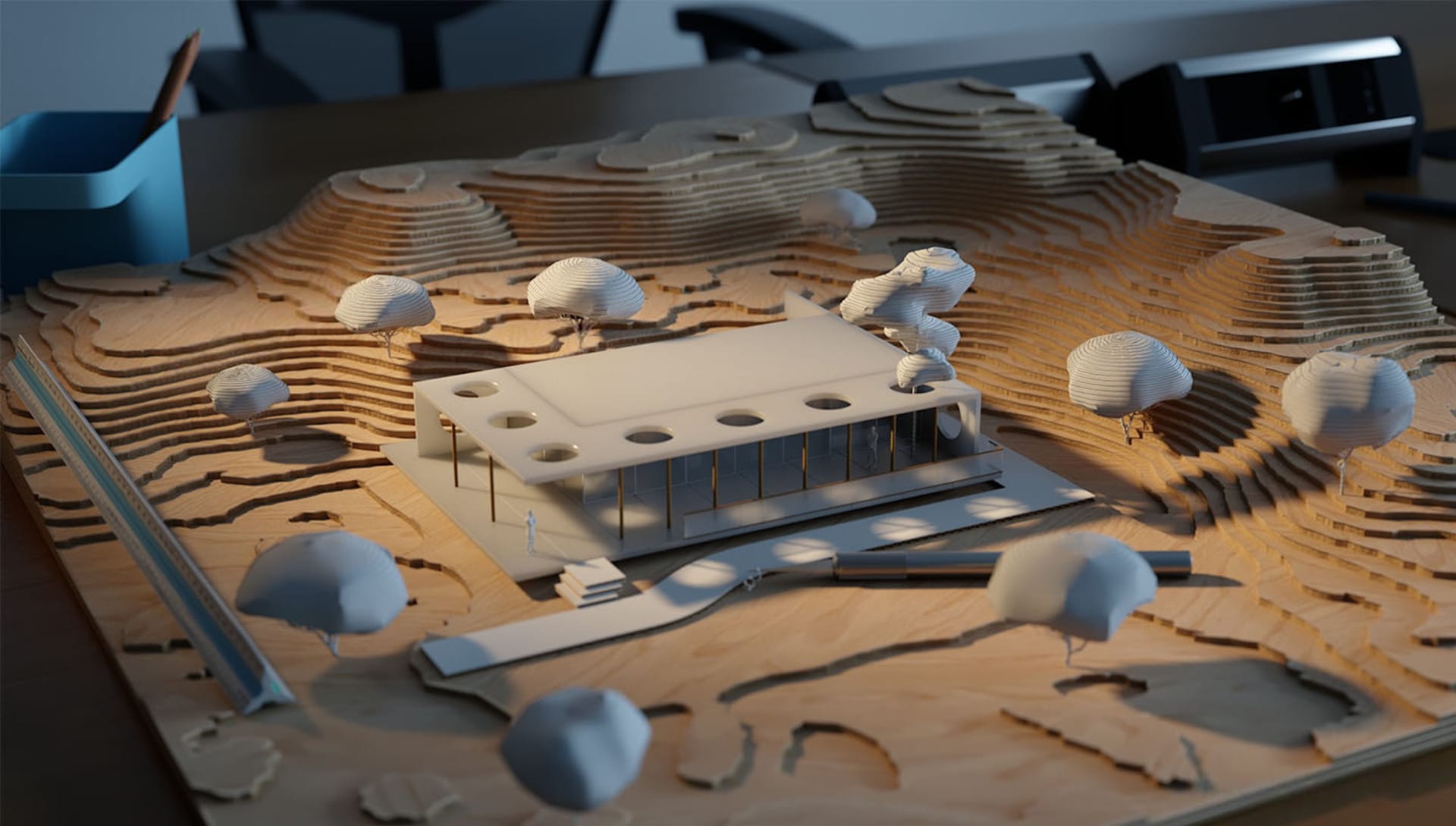

Pros and cons of architectural models
Architectural models and model making offer several advantages and disadvantages:
Pros:
- Tangible representation: Models provide a physical and interactive design representation, allowing viewers to engage with it and gain a better understanding of the spatial qualities.
- Effective communication tool: Models facilitate effective communication between designers, clients, stakeholders, and team members, enabling them to visualize and discuss design concepts.
- Educational and planning purposes: Models are valuable tools in architectural education, urban planning, and historical preservation, allowing for in-depth analysis, evaluation, and exploration of design alternatives.
Cons:
- Time-consuming: Architectural model making can be time-consuming, especially for complex designs.
- Limited flexibility: Once constructed, physical architectural models may be challenging to modify or update, making them less suitable for design iterations.
- Cost: The materials, tools, and expertise required for architectural model making can be costly, especially for large-scale or intricate designs. Spending more time on cementing the conceptual model may help alleviate last minute spending.
- Physical space: Models require physical space for storage and display, which may be a constraint in some situations.
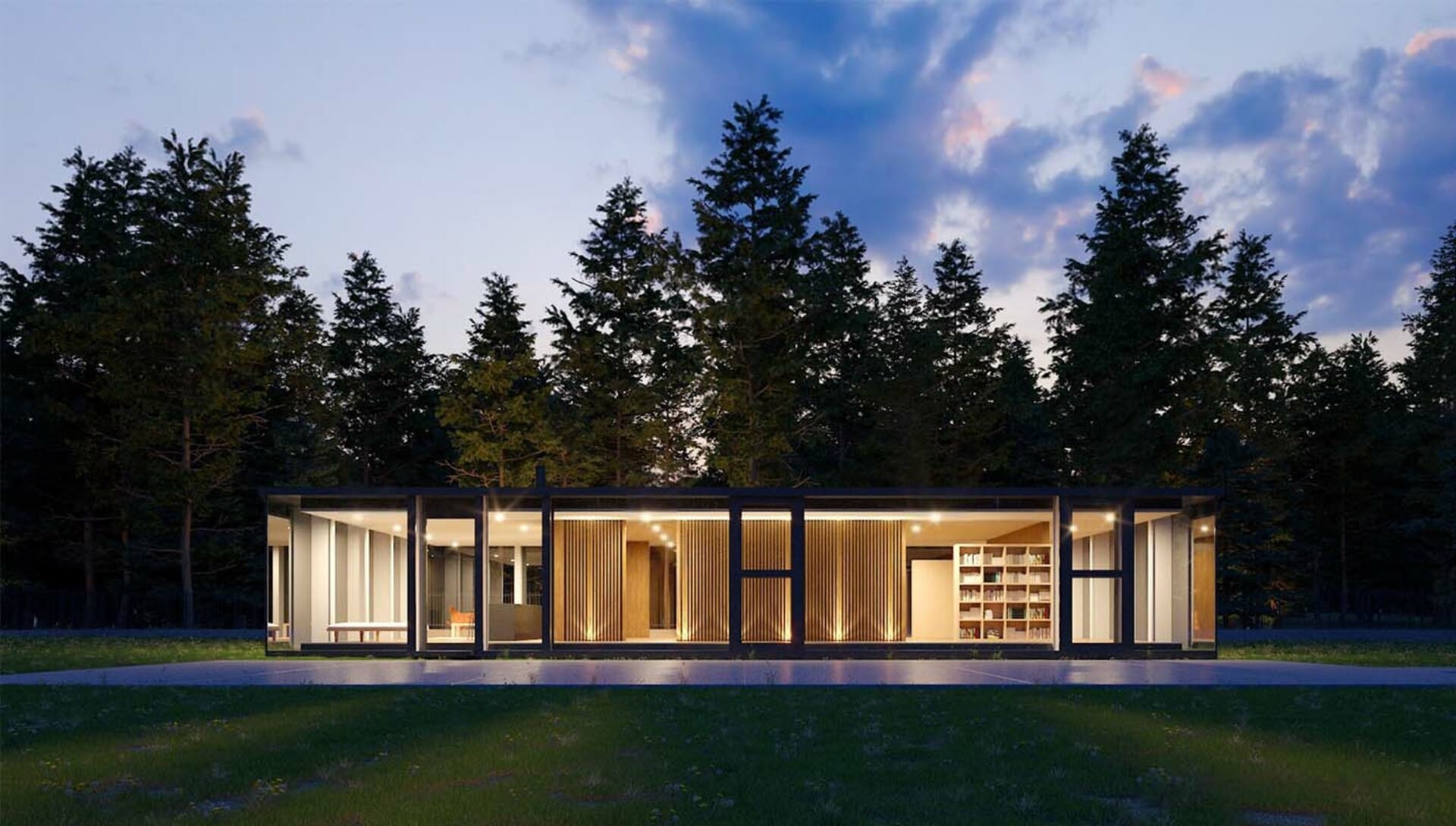

What are architectural renderings?
Architectural renderings are digital visualizations of architectural designs created using software. They play a crucial role in communicating design intent, aesthetics, and spatial qualities of working design model to clients, stakeholders, and team members. Renderings can simulate real-world environments, materials, lighting, and textures, providing a photorealistic result.
Key characteristics
Architectural renderings possess several key characteristics:
- Digital format: Renderings are created and presented in a digital format, allowing for easy sharing, modification, and distribution.
- Software-based: Renderings are generated using specialized software that enables designers to create realistic architectural design visualizations.
- Simulated environments: Renderings can simulate real-world environments, including lighting conditions, materials, textures, and landscaping, providing viewers with a comprehensive understanding of the design.
- Flexibility: Renderings offer flexibility in portraying various design elements, allowing designers to experiment with different materials, colors, lighting scenarios, and perspectives.
- Visualization of complex elements: Renderings can effectively showcase complex architectural elements, such as interior spaces, landscaping, and intricate details, providing a comprehensive design view.
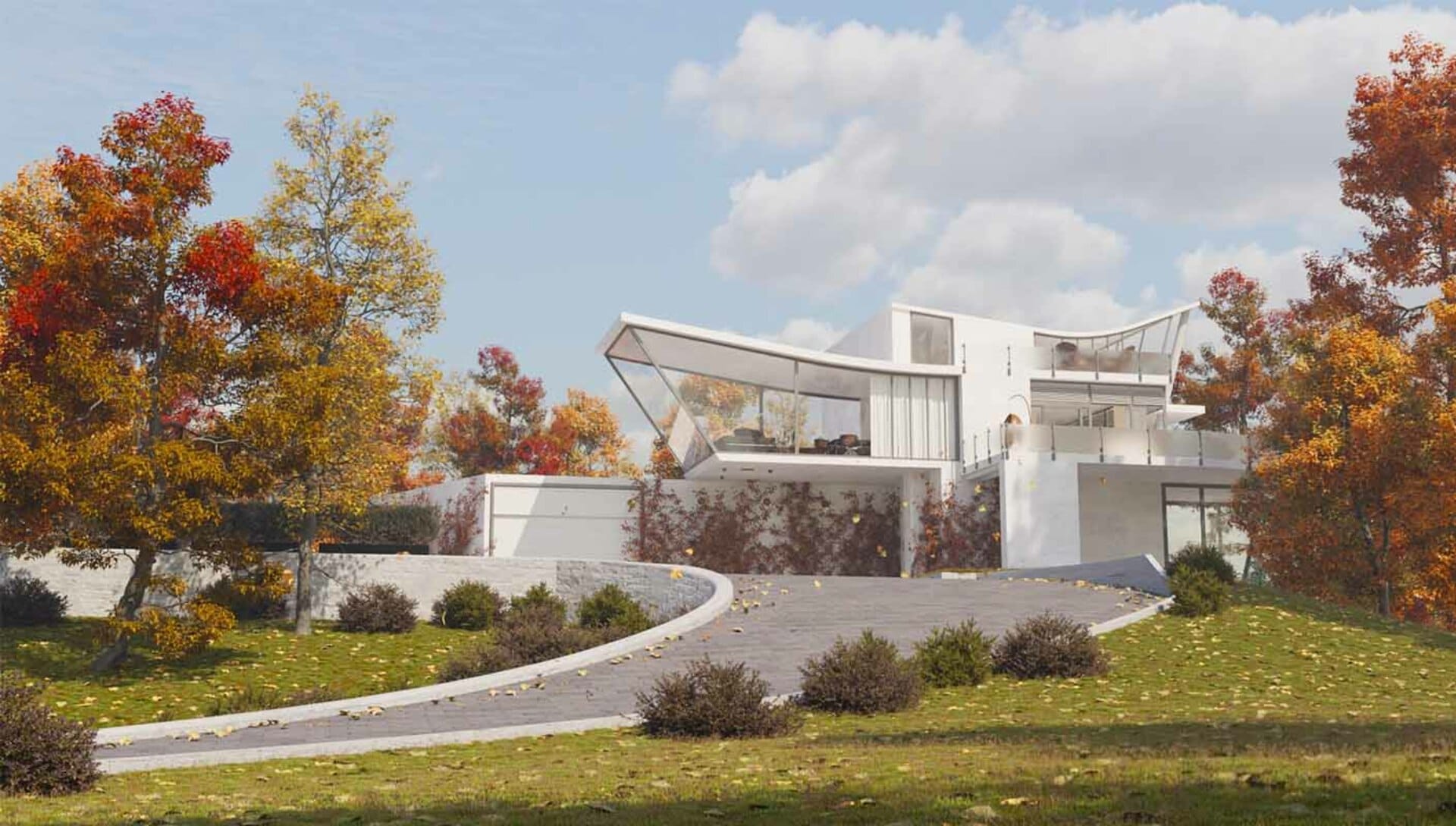

Types of architectural renderings
There are different types of architectural renderings, each serving a specific purpose:
2D renderings
2D renderings are flat representations of architectural designs, often used in floor plans, elevations, and artistic representations of buildings. While they provide a clear visual understanding of the form and shape of the design, they lack the depth and realism of 3D renderings.
3D renderings
3D renderings provide a three-dimensional representation of architectural designs, showcasing depth, textures, lighting, and realistic perspectives. They offer a more immersive and detailed design visualization, allowing viewers to experience the space from different angles, scales, and viewpoints. 3D renderings are commonly used in presentations, marketing materials, and design reviews.
Virtual reality (VR) renderings
VR renderings utilize virtual reality technology to create immersive experiences. Viewers can use VR headsets to explore and navigate the architectural design as if they were physically present within the space. VR renderings provide archviz professionals with a highly interactive and engaging way to experience and evaluate architectural designs.
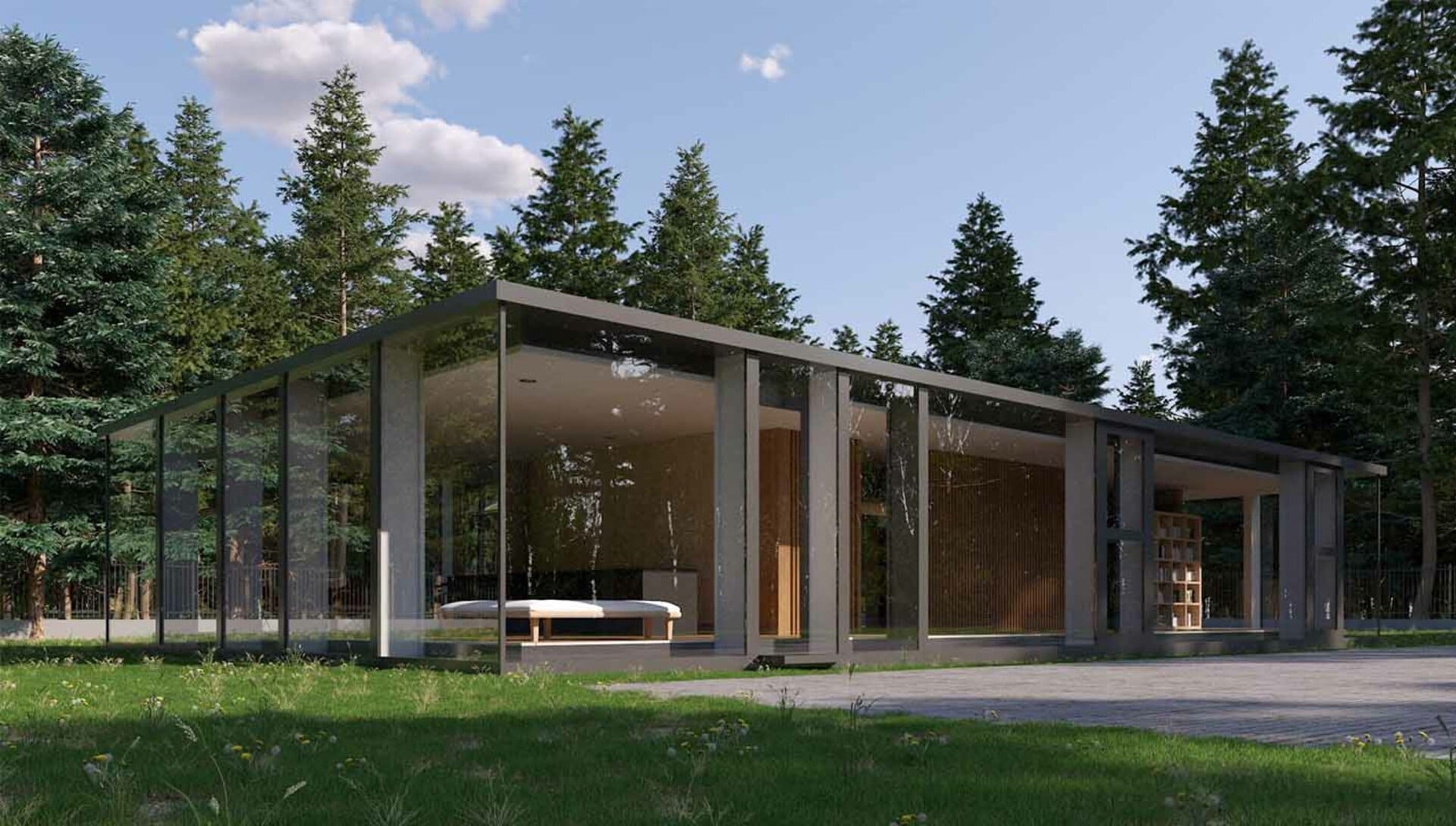

Pros and cons of architectural renderings
Architectural renderings offer several advantages and disadvantages:
Pros:
- Realistic visualization: Renderings provide realistic visualizations of architectural designs, allowing viewers to understand the spatial qualities, materials, lighting, and textures.
- Flexibility and customization: Renderings offer flexibility in experimenting with different design elements, materials, colors, and lighting scenarios, enabling designers to showcase various options.
- Ease of modification: Renderings can be easily modified and updated, making them suitable for design iterations and changes.
- Digital distribution: Renderings can be easily shared digitally, allowing for efficient communication and collaboration among designers, clients, and stakeholders.
Cons:
- Technical expertise: Creating high-quality renderings requires technical expertise in using specialized software and understanding lighting, materials, and rendering techniques.
- Hardware requirements: Rendering complex scenes may require powerful hardware and computing resources.
- Limitations in representing physicality: While renderings provide realistic visualizations, they lack the physicality and tangible experience offered by architectural models.

How to create an architectural rendering
Creating architectural renderings involves several steps and often requires collaboration between architects, 3D artists, and visualization specialists. The process typically includes:
- Design development: Architects develop the design concept and spatial layout of the building or structure.
- 3D modeling: The architectural design is translated into a 3D digital model using specialized software.
- Material and texture application: Materials, textures, and lighting are applied to the 3D model to create a realistic design representation.
- Lighting and rendering setup: Lighting conditions are set up within the software, and the rendering parameters are adjusted to achieve the desired visual outcome.
- Rendering process: The software generates the final rendering by simulating the interaction of light with the 3D model, resulting in a realistic design visualization.
- Post-processing: The rendered image may undergo post-processing techniques such as color correction, image enhancement, and composition adjustments to further refine the visual output.
- Presentation: The completed renderings are presented to clients, stakeholders, or used for marketing purposes to showcase the design intent and spatial qualities.
Check out the full guide on how to create an architectural rendering.
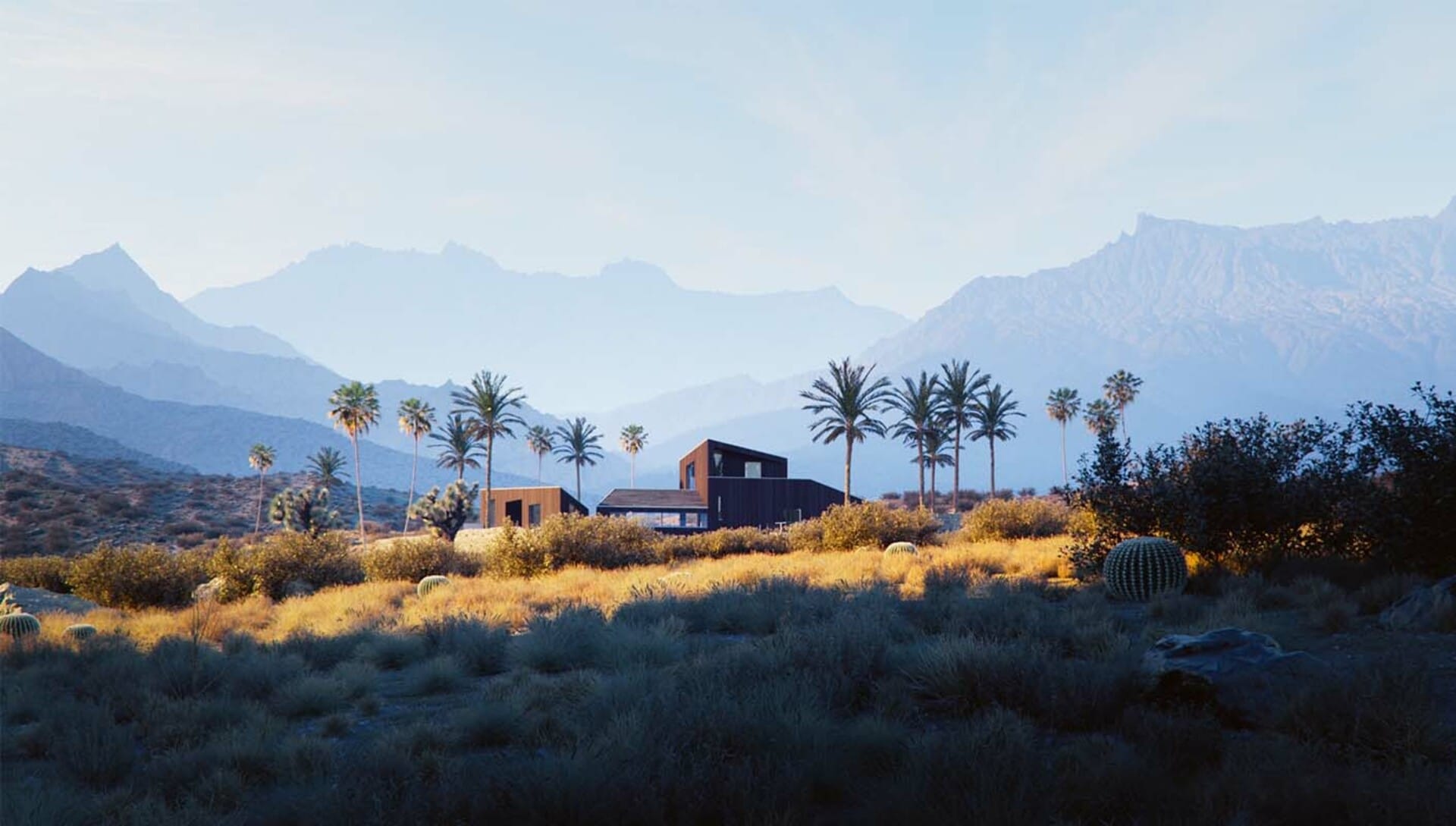

Architectural models vs architectural renderings
Architectural models and renderings have distinct characteristics and serve different purposes. Here are the main differences:
Realism
Architectural models offer a tangible and physical representation of the design, allowing viewers to interact and experience the spatial qualities of the building or structure. On the other hand, architectural renderings serve as a presentation model providing realistic design visualizations using digital software, simulating materials, lighting, and textures.
Interaction and engagement
Architectural models provide a hands-on experience, allowing viewers to physically explore and interact with the design. They offer a tangible understanding of the spatial relationships and proportions. In contrast, architectural renderings offer a visual experience, allowing viewers to observe the design from different angles and perspectives of the presentation model. While renderings lack the physicality of models, they can still engage viewers through realistic visualizations.
Interactivity
Architectural models allow for direct manipulation and modification, making them suitable for design iterations and collaborative discussions. Changes can be made by physically adding or removing elements from the presentation model. On the other hand, architectural renderings are digital representations that can be easily modified and updated using software. They offer flexibility in experimenting with different design elements, materials, colors, and lighting scenarios.
Cost and time spent
Creating architectural models can be time-consuming and costly, especially for complex designs that require intricate detailing and craftsmanship. The materials, tools, and expertise required for model construction contribute to the overall cost and should be planned in the beginning of the design process. Architectural renderings, while also requiring time and expertise, can be more cost-effective in terms of material expenses. However, the design complexity and the level of detail required can impact the time spent on rendering.
Flexibility
Architectural models have limitations in flexibility once constructed. Modifications or updates may require significant effort or even rebuilding the model. In contrast, architectural renderings offer greater flexibility as they can be easily modified and updated digitally. Changes can be made to materials, lighting, textures, and other design elements without the need to recreate the entire visualization.
Design iterations
Architectural models are well-suited for design iterations and collaborative discussions. They allow for direct physical manipulation and exploration, enabling designers and stakeholders to evaluate different design options and make informed decisions. Architectural renderings, with their flexibility and ease of modification, also support design iterations. Changes can be made digitally, allowing for quick visualization of alternative design concepts.
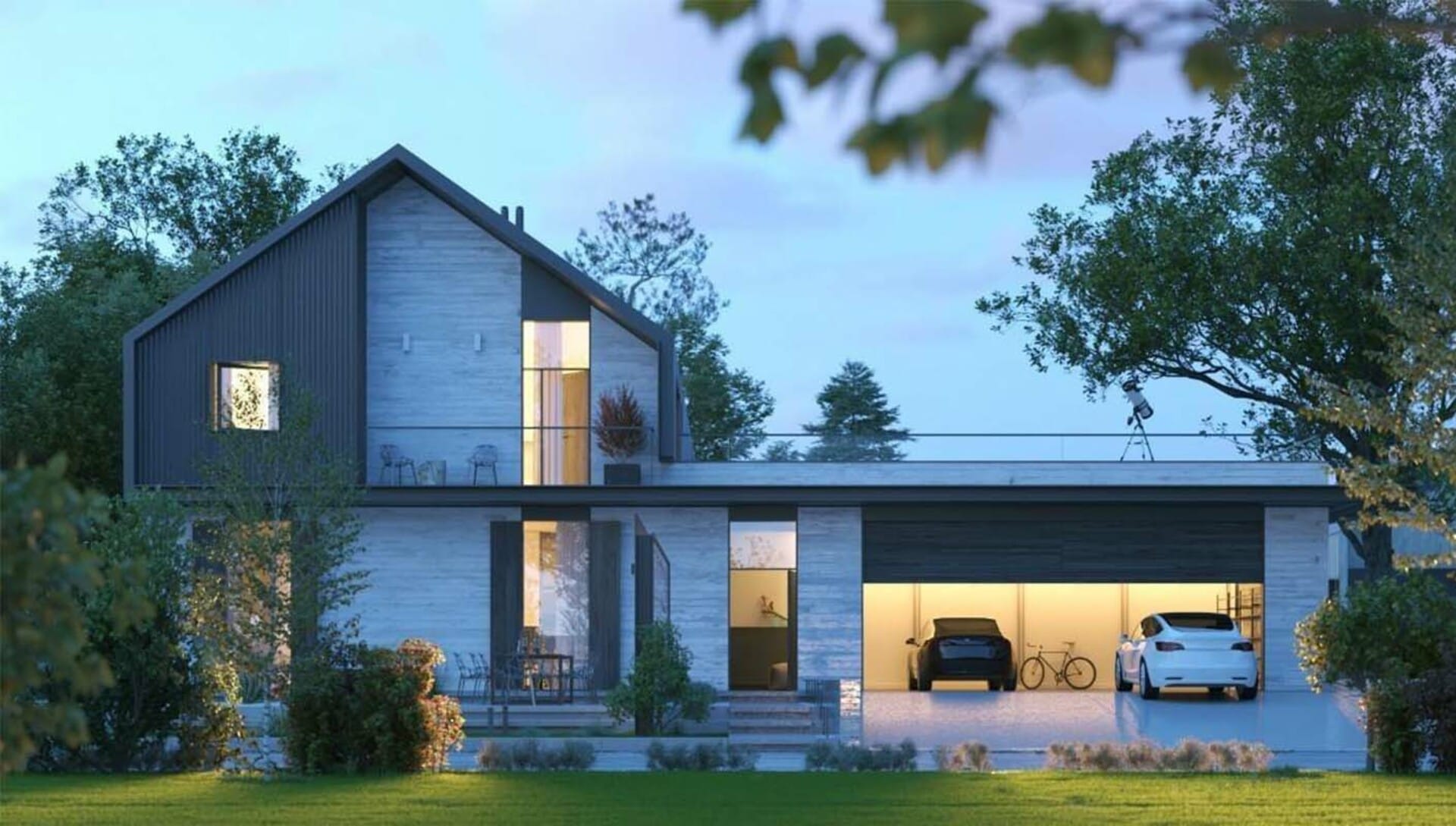

Complementary roles in design visualization
Architectural models and renderings play complementary roles in building and presenting design concepts:
- Architectural models: Models provide a tangible and interactive representation of the design, allowing viewers to physically engage with the spatial qualities and proportions. They are particularly useful in early design stages as presentation models, allowing designers to explore ideas, communicate concepts, and evaluate spatial relationships. Models are also valuable in architectural education, urban planning, and historical preservation, enabling in-depth analysis and evaluation of design alternatives.
- Architectural renderings: Renderings offer realistic design visualizations, showcasing materials, lighting, textures, and other design elements. They are effective in communicating design intent, aesthetics, and spatial qualities to clients, stakeholders, and team members. Renderings are commonly used in presentations, marketing materials, and design reviews. They provide a comprehensive design view, allowing viewers to understand the overall composition and experience the space virtually.
In many cases, models and renderings are used in tandem to enhance the architectural visualization process. Models provide a physical representation for hands-on exploration, while renderings offer realistic visualizations for a comprehensive design understanding. For example, models can be used in early design stages to explore ideas and spatial relationships, while renderings to showcase the final design intent and aesthetics.
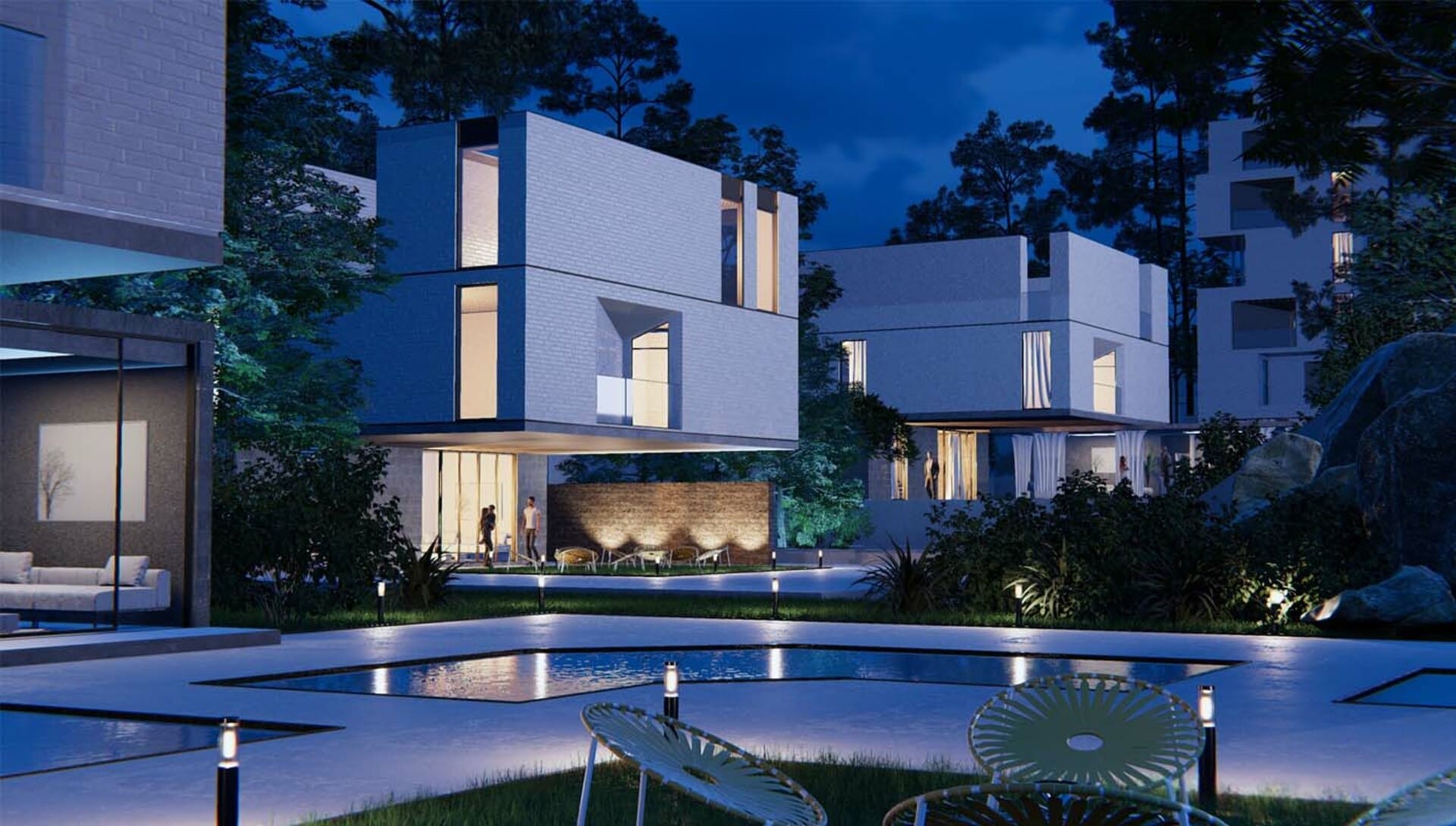

Choosing between architectural models and architectural renderings
Several factors influence the choice between architectural models and renderings:
- Project scale: For large-scale projects, architectural renderings may be more practical and cost-effective, as creating physical models for such projects can be time-consuming and expensive. Smaller-scale projects may benefit from physical models, as they provide a tangible design representation.
- Client preferences: Some clients may prefer the interactive nature of physical presentation models, while others may appreciate the realism and flexibility of renderings. Understanding client preferences and requirements is crucial in determining the appropriate visualization method.
- Budget: The available budget can impact the choice between models and renderings. Physical models require materials, tools, and craftsmanship, which can be costly. Renderings, while still requiring expertise and software, may be more cost-effective in terms of material expenses.
- Timeline: The project timeline can also influence the choice between models and renderings. Creating detailed physical models can be time-consuming, especially for complex designs. Renderings, on the other hand, can be generated relatively quickly using specialized software.
It is important to consider these factors and evaluate the specific needs of each project when deciding between architectural models and renderings. In some cases, a combination of both may be advantageous, utilizing models and renderings at different project stages to effectively communicate design concepts and spatial qualities.
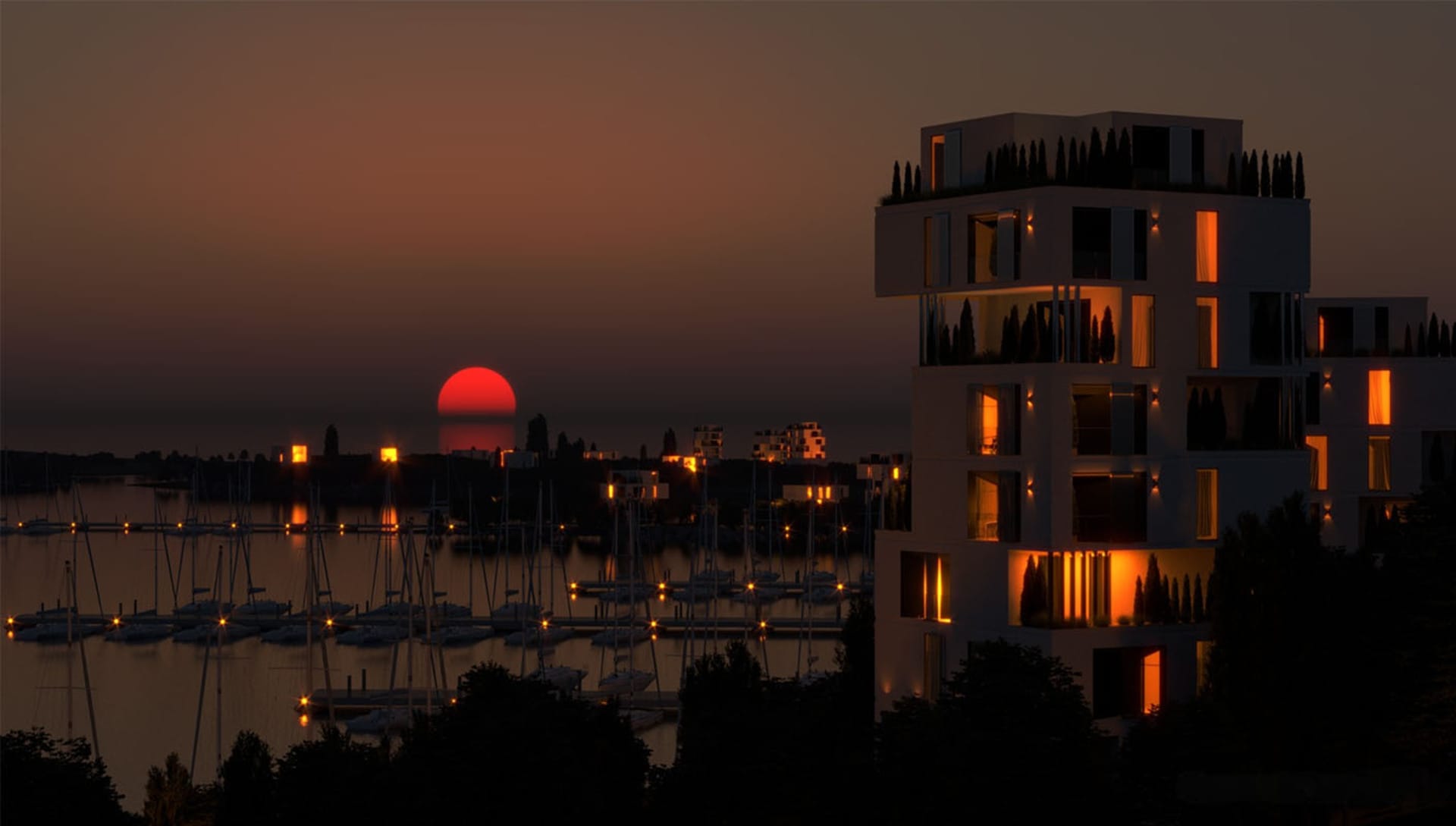

Embrace the synergy of architectural models and renders
Both architectural models and architectural renderings play crucial roles in visualizing and communicating design concepts in architecture. Architectural models offer a tangible and interactive experience, allowing viewers to physically engage with the design and understand spatial qualities. On the other hand, architectural renderings provide realistic digital visualizations, showcasing materials, lighting, and textures. Each has its own advantages and considerations, such as cost, time spent, flexibility, and design iterations.
However, when used together, models and renderings can enhance the design visualization process by providing a comprehensive design understanding from both physical and digital perspectives. By utilizing the unique characteristics of these tools, architects can effectively communicate their design concepts to clients, stakeholders, and team members. Whether it's the physicality and detail of models or the realism of renderings, both contribute to creating successful architectural designs.